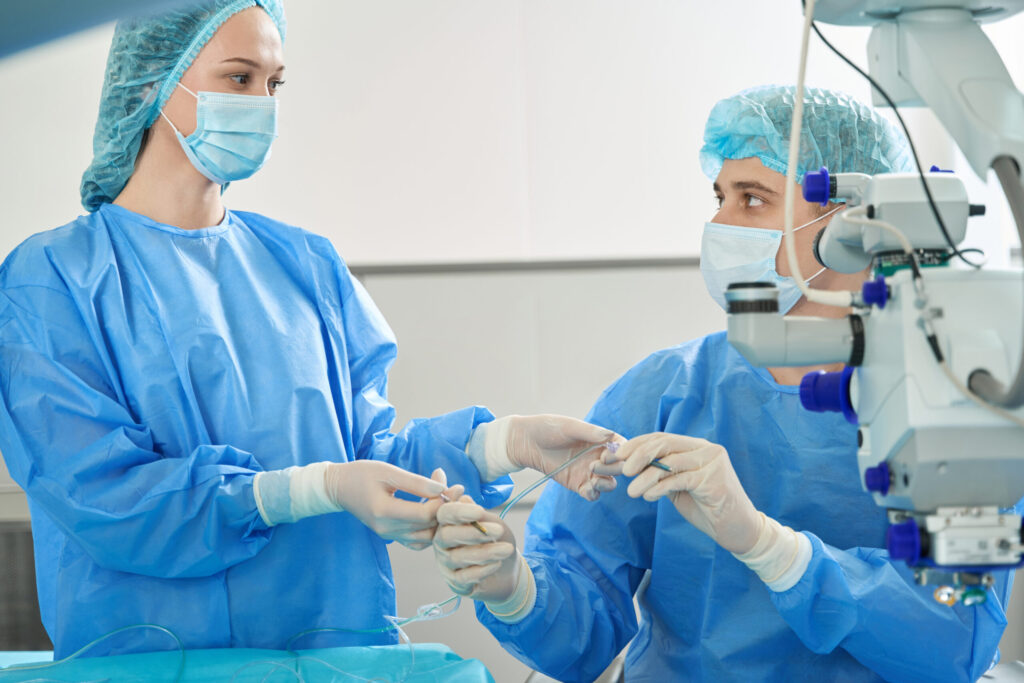
Glaucoma is a serious eye condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is one of the leading causes of blindness, but with early detection and proper treatment, vision loss can be prevented or minimized. Understanding glaucoma, the diagnosis process, preparing for surgery, the procedure itself, and post-surgery care are crucial steps in navigating the journey from diagnosis to recovery.
Understanding Glaucoma Surgery
There are several surgical options for treating glaucoma, and the choice depends on the specific type and severity of glaucoma. Some common types of glaucoma surgery include trabeculectomy, minimally invasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS), and laser surgery. Trabeculectomy involves creating a new drainage channel to allow fluid to drain out of the eye, thus reducing intraocular pressure (IOP). Minimally invasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS) utilizes tiny devices to improve the eye’s natural drainage system. Laser surgery, such as selective laser trabeculoplasty (SLT), helps to increase the outflow of fluid from the eye, lowering the IOP and protecting the optic nerve.
What is Glaucoma?
Glaucoma is a complex group of eye diseases that affect the optic nerve, a crucial component of the visual system. The optic nerve is responsible for transmitting visual information from the eye to the brain, allowing us to see the world around us. When damage occurs to the optic nerve, typically due to increased pressure inside the eye, it can lead to irreversible vision loss if left untreated. This increased pressure, known as intraocular pressure (IOP), can gradually cause damage to the optic nerve fibers, resulting in vision impairment.
Aside from primary open-angle glaucoma, which is the most common type, there are other variations of glaucoma, such as angle-closure glaucoma and normal-tension glaucoma. Each type has its own unique characteristics and treatment approaches, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis and personalized care.
The Causes and Risk Factors of Glaucoma
While the precise cause of glaucoma remains elusive, researchers have identified several risk factors that can predispose individuals to developing this sight-threatening condition. Advancing age is a significant risk factor, as the likelihood of developing glaucoma increases with age. Additionally, individuals with a family history of glaucoma are at higher risk, suggesting a genetic component to the disease. Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes and hypertension, can also contribute to the development of glaucoma. Furthermore, long-term use of corticosteroids, whether in the form of eye drops or systemic medications, can elevate intraocular pressure and increase the risk of glaucoma. By understanding these risk factors, individuals can work with their healthcare providers to implement preventive strategies and regular eye screenings to safeguard their vision. Raed more about genetic component at https://learn.genetics.utah.edu/
Moreover, ongoing research is exploring potential links between lifestyle factors, such as diet, exercise, and smoking, and the development of glaucoma. By adopting a healthy lifestyle and staying informed about the latest advancements in glaucoma research, individuals can actively participate in preserving their eye health and overall well-being.
Common Symptoms and Signs of Glaucoma
Glaucoma is often referred to as the “silent thief of sight” because it can progress stealthily without causing noticeable symptoms in the early stages. However, as the condition advances, individuals may experience a variety of symptoms that signal potential damage to their vision. These symptoms can include blurred vision, eye pain, redness, halos around lights, and a gradual narrowing of the field of vision. It is crucial for individuals, especially those at higher risk for glaucoma, to undergo regular comprehensive eye examinations to detect any signs of glaucoma early. Early detection enables prompt intervention and management, which are vital in preserving vision and maintaining eye health in the long run.
The Glaucoma Diagnosis Process
When it comes to diagnosing glaucoma, a multi-faceted approach is often necessary. In addition to the standard tests like tonometry, visual field testing, optic nerve evaluation, and imaging tests, there are other specialized examinations that may be employed. These can include gonioscopy to assess the drainage angle of the eye, pachymetry to measure the thickness of the cornea, and even genetic testing in certain cases to identify hereditary factors that may contribute to glaucoma development.
Each of these tests provides valuable insights into different aspects of the disease, allowing your eye doctor to form a comprehensive understanding of your condition. By combining the results of these various tests, a more accurate diagnosis can be made, leading to more effective management strategies.
Different Types of Glaucoma Tests
A variety of tests are used to diagnose glaucoma and evaluate its progression. These tests may include tonometry to measure IOP, visual field testing to assess peripheral vision, optic nerve evaluation, and imaging tests such as optical coherence tomography. Your eye doctor will determine which tests are most appropriate based on your symptoms and risk factors.
Interpreting Your Glaucoma Test Results
Understanding the results of your glaucoma tests is crucial for making informed decisions about treatment options. Your eye doctor will explain the significance of your test results, including the level of damage to your optic nerve and the severity of your glaucoma. Together, you can develop a personalized treatment plan.
Preparing for Glaucoma Surgery
Pre-Surgery Consultation and Evaluation
Prior to undergoing glaucoma surgery, you will have a consultation with your ophthalmologist to discuss the details of the procedure and address any concerns or questions you may have. Your eye doctor will also evaluate your overall health and determine if there are any specific precautions or preparations you need to take. During this consultation, your ophthalmologist will explain the potential risks and benefits of the surgery, as well as the expected outcomes. They will also review your medical history and current medications to ensure a safe surgical experience. To find more about potential risks click here.
Furthermore, the ophthalmologist may perform additional tests, such as visual field testing and optical coherence tomography (OCT), to assess the extent of optic nerve damage and monitor the progression of glaucoma. These tests help in determining the most suitable surgical approach tailored to your individual needs.
What to Expect on the Day of Surgery
On the day of your glaucoma surgery, you will be provided with specific instructions regarding fasting, medication usage, and arrival time. The surgical team will guide you through the pre-surgical preparations and ensure that you are comfortable and well-informed every step of the way. You will have the opportunity to ask any last-minute questions and address any concerns before the procedure begins. The surgical staff will also explain the post-operative care instructions and schedule any necessary follow-up appointments to monitor your recovery progress.
The Glaucoma Surgery Procedure
Glaucoma surgery is a crucial intervention aimed at managing intraocular pressure (IOP) to prevent further optic nerve damage and vision loss. The decision to undergo glaucoma surgery is often made when other treatment options, such as medications or laser therapy, have not effectively controlled the progression of the disease.
The Role of Anesthesia in Glaucoma Surgery
Glaucoma surgery can be performed under local anesthesia, which numbs the eye area, or general anesthesia, which induces temporary unconsciousness. The choice of anesthesia depends on factors such as patient preference, the specific procedure being performed, and the surgeon’s recommendation. Local anesthesia is commonly preferred for its quicker recovery time and reduced risks associated with general anesthesia.
Before the administration of anesthesia, the surgical team conducts a thorough pre-operative assessment to ensure the patient’s safety and comfort throughout the procedure. An anesthesiologist plays a crucial role in monitoring the patient’s vital signs and adjusting the anesthesia levels as needed to maintain optimal conditions during surgery.
Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Surgery
The specifics of glaucoma surgery can vary depending on the technique being used. However, the general goal is to create an alternate drainage pathway to reduce IOP. This may involve creating a small opening in the eye’s drainage system, using a drainage implant, or applying laser technology to increase the outflow of fluid.
During the procedure, the surgeon meticulously performs each step with precision to ensure the best possible outcome for the patient. Advanced surgical tools and technologies are utilized to enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of the surgery. Post-operative care is equally important, with regular follow-up appointments scheduled to monitor the eye’s healing process and IOP levels.
Post-Surgery Care and Recovery
Immediate Post-Surgery Care
After glaucoma surgery, you will be given detailed instructions for post-operative care to promote healing and minimize the risk of complications. This may include using prescribed eye drops, avoiding strenuous activities, wearing protective eyewear, and attending follow-up appointments to monitor your progress.
It is crucial to follow these instructions diligently to ensure a smooth recovery process. Proper care post-surgery can significantly impact the success of the procedure and the overall health of your eyes. In addition to the mentioned precautions, maintaining good hygiene practices, such as washing your hands before administering eye drops, can help prevent infections and aid in the healing process.
Long-Term Recovery and Lifestyle Adjustments
While glaucoma surgery can effectively control IOP and preserve vision, it is important to recognize that glaucoma cannot be cured. Ongoing management and regular follow-up care are essential to maintain the health of your eyes and prevent future vision loss. Lifestyle adjustments, such as protecting your eyes from injury and managing other health conditions, can also contribute to long-term recovery.
Furthermore, incorporating a balanced diet rich in nutrients like vitamin C, vitamin E, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids can support eye health and overall well-being. Regular exercise, as recommended by your healthcare provider, can also improve blood flow to the eyes and help in the recovery process post-surgery. Remember, a holistic approach to recovery involves not only medical interventions but also lifestyle choices that promote overall health.
Other resources: Comprehensive Care How Glaucoma Surgery Can Preserve Your Vision